Mauritania travel tips
Mauritania travel tips: In North Africa, features vast desert landscapes, diverse ethnicities, ancient caravan routes, and a nomadic culture rich in tradition.
Regions 🌎
Mauritania travel tips. Here is a list of all the regions of the Mauritania.
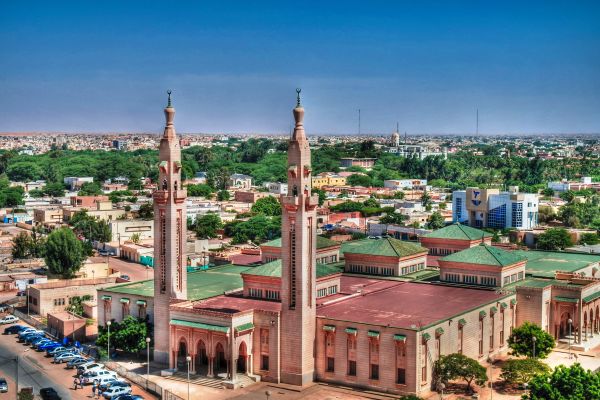

Nouakchott
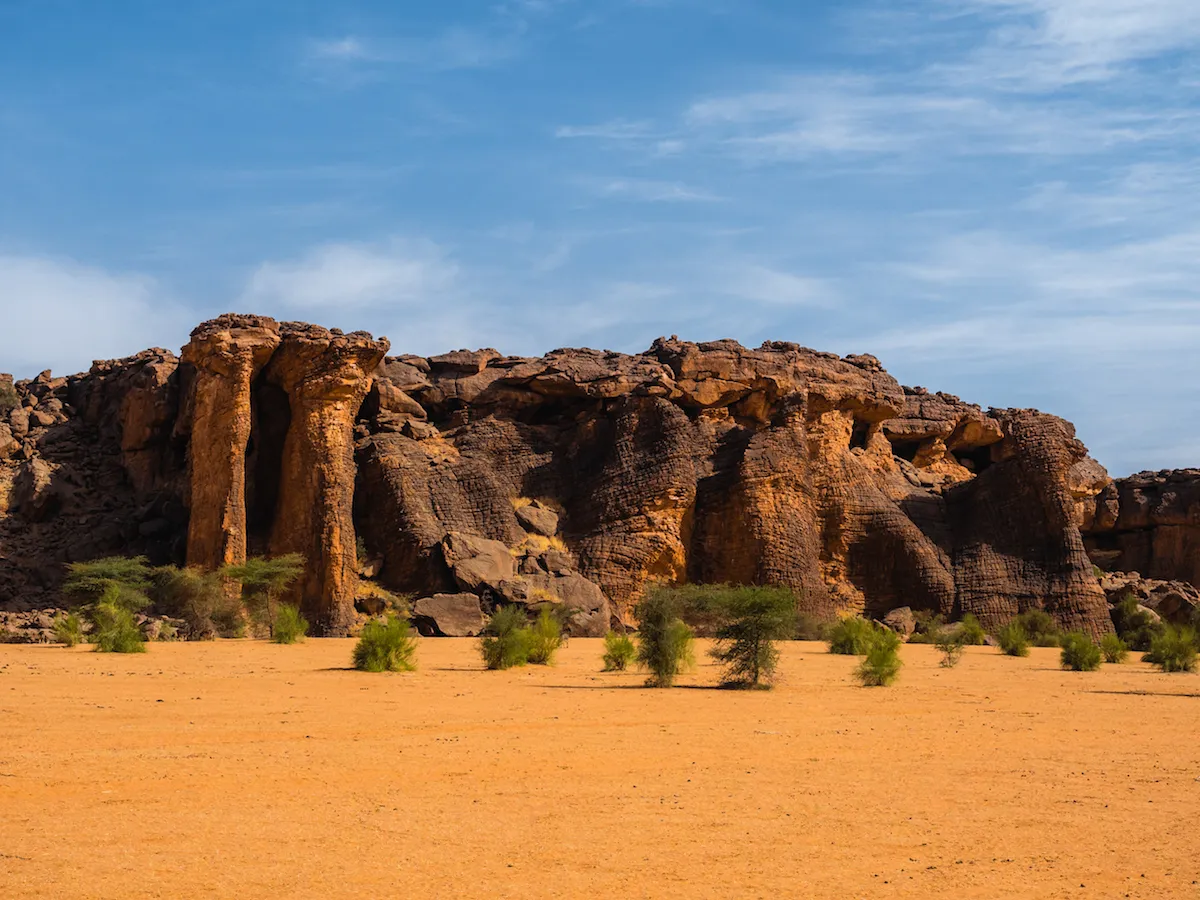

Hodh Elgharbi

Hodh Ech Chargui

Assaba
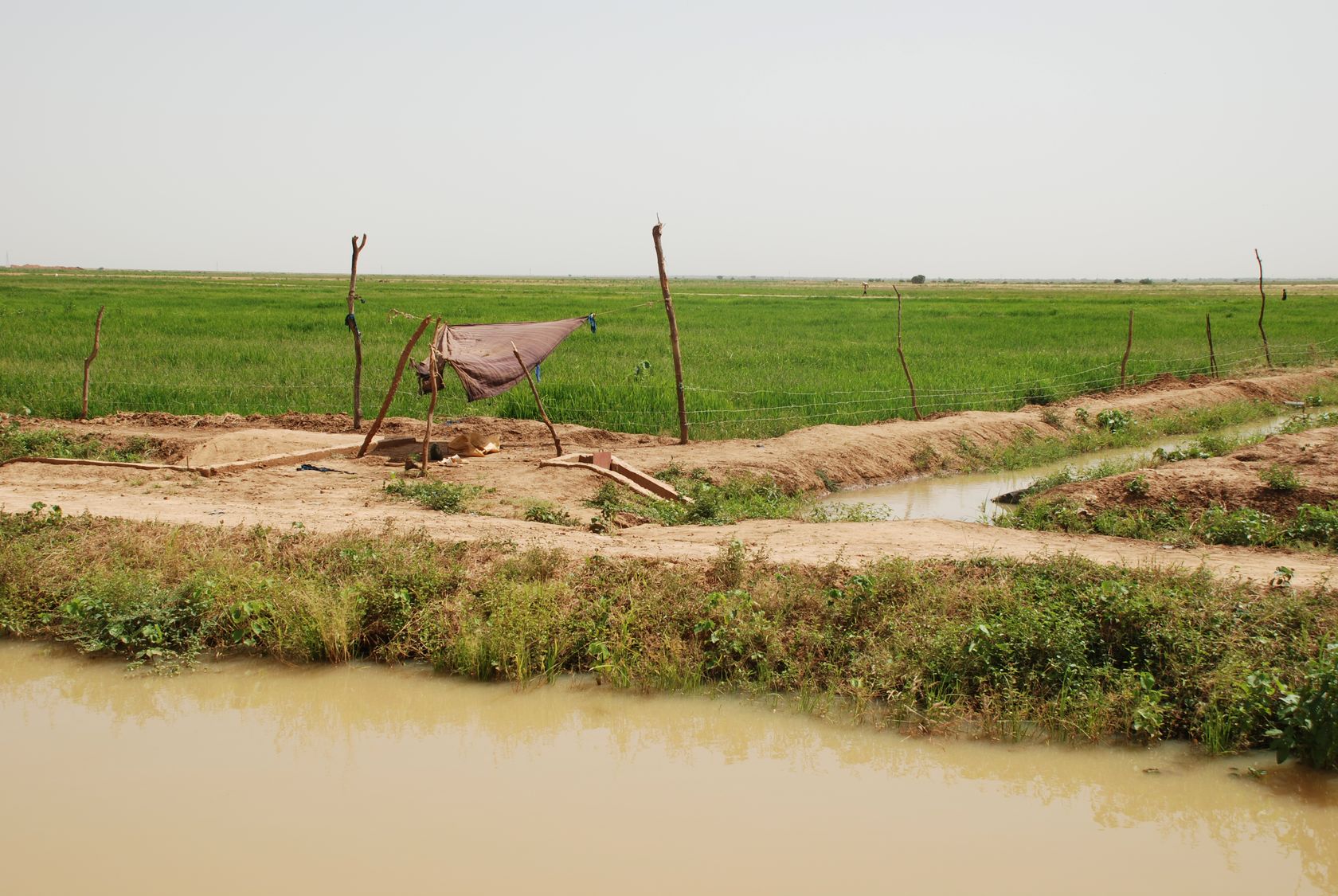

Gorgol
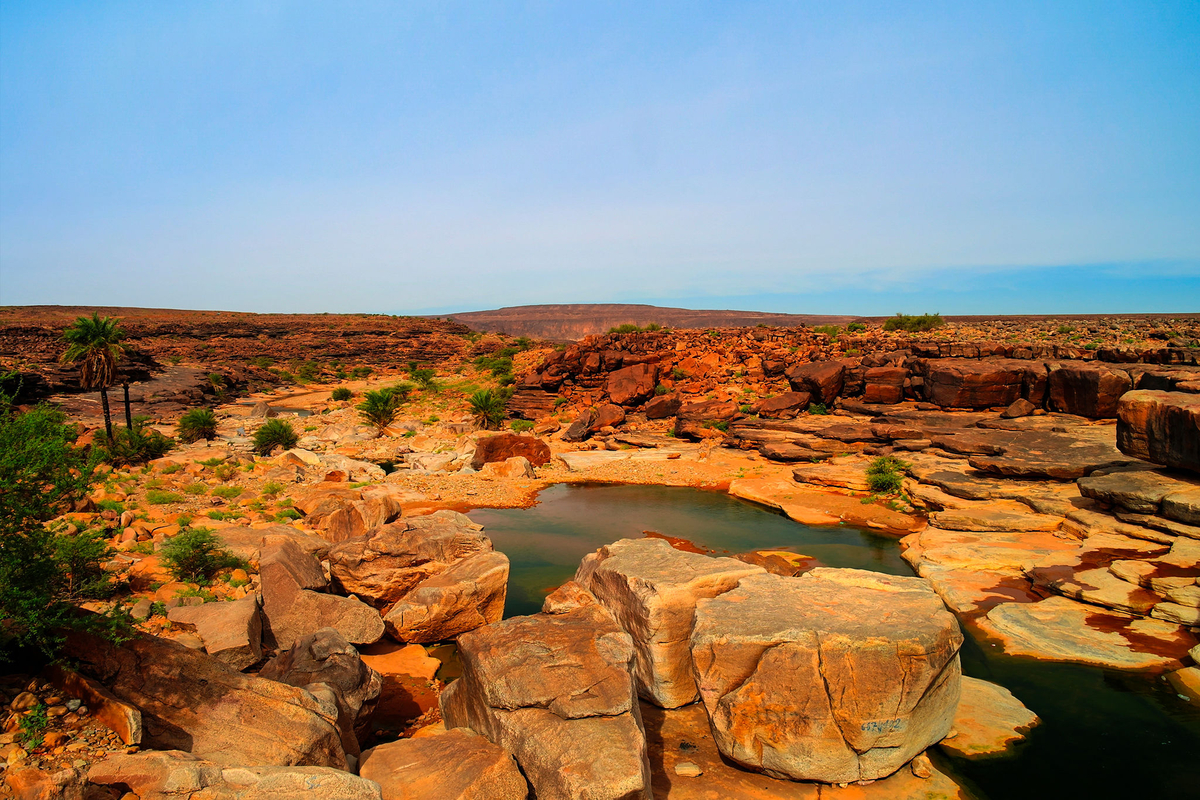

Brakna

Trarza

Adrar

Tagant

Guidimaka

Tiris Zemmour

Inchiri

Dakhlet Nouadhibou
Before you go 🛩
Important information you should know before your trip
Info

Capital | Nouakchott
Flag Codes:
ISO alpha-2 MR,
ISO alpha-3 MRT
Currency
Badge | Ouguiya
CODE | MRO
NUMBER | 478
SYMBOL | UM
FRACTION | jum
Mobile Coverage
Dialing Code | +212
SIM Card
Coverage | 3G / 4G / 5G |
Mobile Networks | Chinguitel | Mattel | Mauritel Mobile |
Location
Mauritania is a country located in West Africa. It is situated on the northwest coast of the African continent, with a coastline along the Atlantic Ocean to the west.
The capital city of Mauritania is Nouakchott, which is located on the country’s Atlantic coast. Nouakchott is the largest city in the country and serves as its administrative and economic center.
Mauritania’s geography is characterized by vast desert expanses, including portions of the Sahara Desert, which cover a significant portion of the country’s inland areas. The country’s landscape includes desert dunes, plateaus, and arid regions, with the Sahara Desert extending into the northern and eastern parts of Mauritania. In contrast, the coastal regions, particularly in the west, have a more moderate climate and are home to a majority of the population.
Currency
The official currency of Mauritania is the Mauritanian Ouguiya, abbreviated as MRU. The currency is represented by the symbol “UM,” and its ISO 4217 currency code is “MRU.” The Mauritanian Ouguiya is further subdivided into smaller units called “khoums.” One ouguiya is equal to five khoums.
Please note that currency exchange rates can fluctuate, so it’s a good practice to check with reliable financial sources or currency exchange services for the most up-to-date exchange rates when dealing with foreign currencies, including the Mauritanian Ouguiya.
Languages
The official language of Mauritania is Arabic. Arabic is used in government, education, media, and official documents. However, it’s important to note that Mauritania is a linguistically diverse country with several ethnic groups, and different languages are spoken by various communities. Some of the other languages spoken in Mauritania include:
Hassaniya Arabic: Hassaniya Arabic, a variety of Arabic, is the most widely spoken language in Mauritania. It is the mother tongue of many Mauritanians, particularly in the western and southern regions of the country.
Pulaar (Fulfulde): Pulaar, also known as Fulfulde or Fula, is spoken by the Fulani people and is one of the major indigenous languages of Mauritania. It is primarily spoken in the southern and eastern regions of the country.
Soninke: Soninke is spoken by the Soninke people in southern Mauritania, particularly in the regions bordering Senegal and Mali.
Wolof: Wolof is spoken by the Wolof ethnic group, primarily in urban areas and along the Senegal River.
French: French is also widely used in Mauritania, especially in formal education and business contexts. It is the second official language and is taught in schools.
Hassani: Hassani is a regional variant of Arabic spoken in some parts of southern Mauritania, particularly among the Maures, who are of Arab-Berber descent.
The linguistic diversity in Mauritania reflects the country’s multicultural and multiethnic composition. While Arabic is the official language and the lingua franca for communication across different ethnic groups, various indigenous languages are spoken by specific communities, especially in rural areas. French serves as a language of instruction and administration.
Climate 🌡
Mauritania’s climate varies across different regions of the country due to its geographical diversity, with desert, semi-arid, and Sahelian climates. Here’s an overview of the climate in Mauritania:
Saharan Desert Climate: Northern Mauritania is part of the Sahara Desert, characterized by an extreme desert climate. This region experiences extremely hot and dry conditions throughout the year, with temperatures often exceeding 40°C (104°F) during the day. Nights can be much cooler. Rainfall is extremely scarce, and the desert landscape is dominated by sand dunes and rocky plateaus.
Semi-Arid Climate: The central and eastern parts of Mauritania, including the Adrar Plateau and areas near the border with Mali, have a semi-arid climate. Summers are hot and dry, with daytime temperatures often exceeding 40°C (104°F). Winters are relatively cooler. Rainfall is low and erratic, with occasional droughts.
Sahelian Climate: The southern regions of Mauritania, particularly along the Senegal River valley, have a Sahelian climate. This area experiences a distinct wet season from July to October, during which rainfall is more consistent. Temperatures are generally milder than in the desert regions, and agricultural activities are more viable. The Sahelian region is the most agriculturally productive part of the country.
Coastal Climate: Mauritania’s western coastline along the Atlantic Ocean has a coastal climate characterized by milder temperatures and higher humidity compared to the inland desert areas. Coastal areas, including the capital city Nouakchott, have a Mediterranean-influenced climate with relatively mild summers and cooler winters. Rainfall is more consistent along the coast.
Wind and Dust: Throughout Mauritania, strong and sometimes dusty winds are common, particularly during the dry season. These winds can bring sand and dust storms, impacting visibility and creating challenging conditions, especially in desert regions.
Mauritania travel tips
If you’re planning a trip to Mauritania, here are some travel tips to enhance your experience:
Visas and Documentation:
Check visa requirements and have necessary travel documents, including a passport and any required permits.
Local Customs:
Respect Islamic traditions; dress modestly, especially in rural areas, and ask for permission before taking photos.
Cultural Sensitivity:
Follow local customs, avoid public displays of affection, and be respectful of local norms.
Bargaining:
Bargain in markets but do so respectfully; it’s a common practice.
Transportation:
Arrange reliable transportation in advance; public transport is limited, and desert conditions can be challenging. View Guide.
Guides for Tours:
Consider hiring local guides for desert tours; they offer valuable insights into the terrain and culture.
Natural Landscapes:
Explore the diverse landscapes, from the Sahara Desert to the Banc d’Arguin National Park.
Enjoy your time in Mauritania!

The best of the best
Mauritanian cuisine reflects the country’s nomadic and Saharan influences, with an emphasis on grains, dairy products, and meat. The cuisine is simple yet flavorful, making use of available ingredients in the arid desert climate.
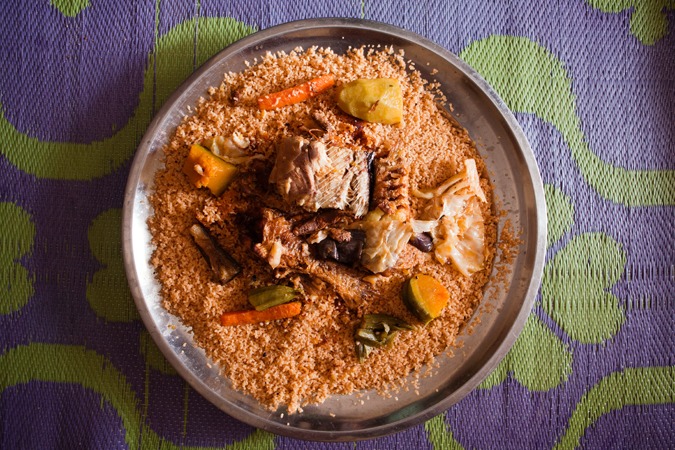

Thiéboudienne
Thiéboudienne is often considered the national dish of Mauritania. It’s a flavorful fish and rice dish cooked with vegetables and spices, often featuring ingredients like tomatoes, okra, and chili peppers.
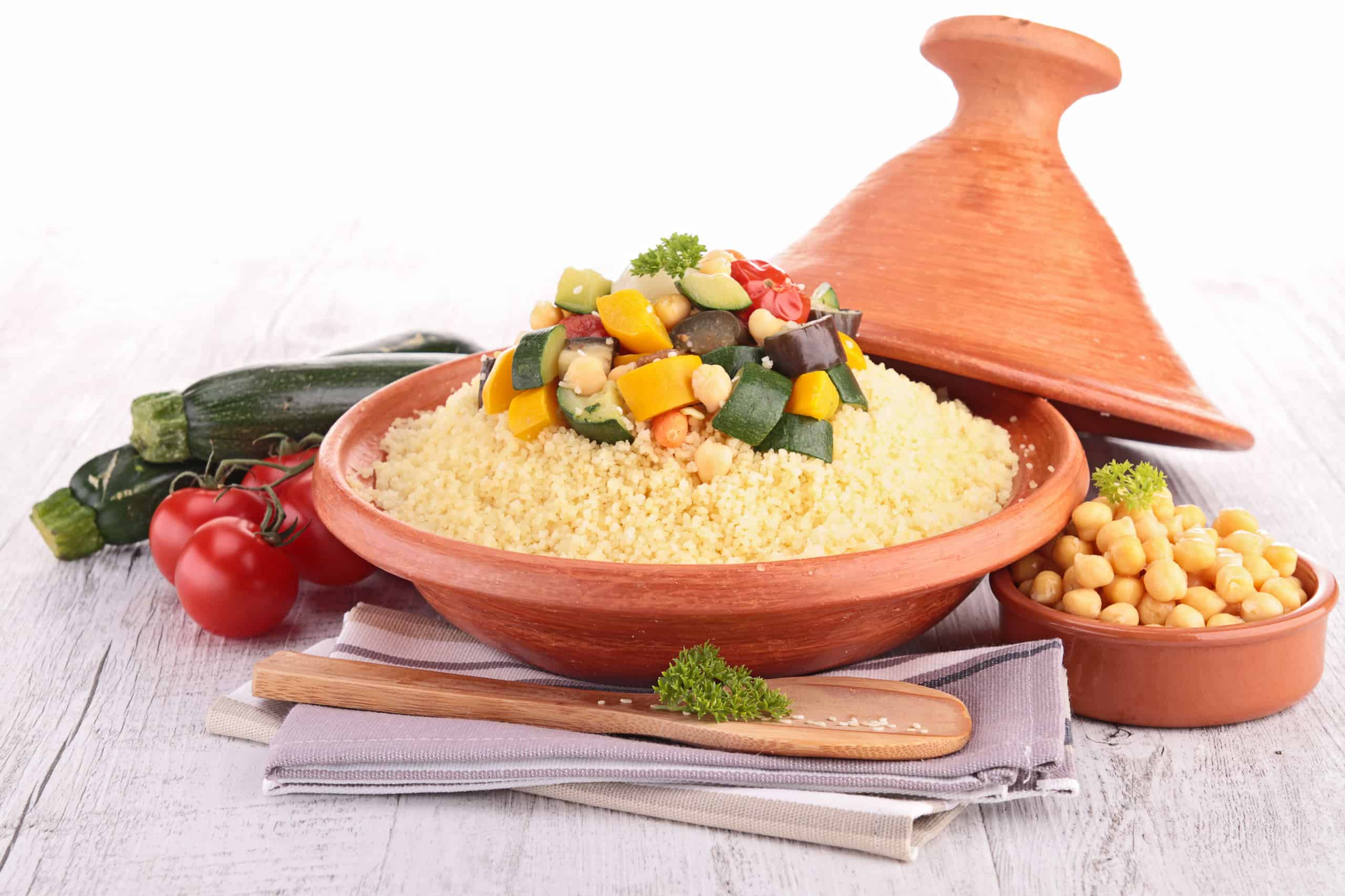

Couscous
Couscous is a staple food in Mauritania, usually served with a meat or vegetable stew. It may be made from millet or wheat, depending on the region.
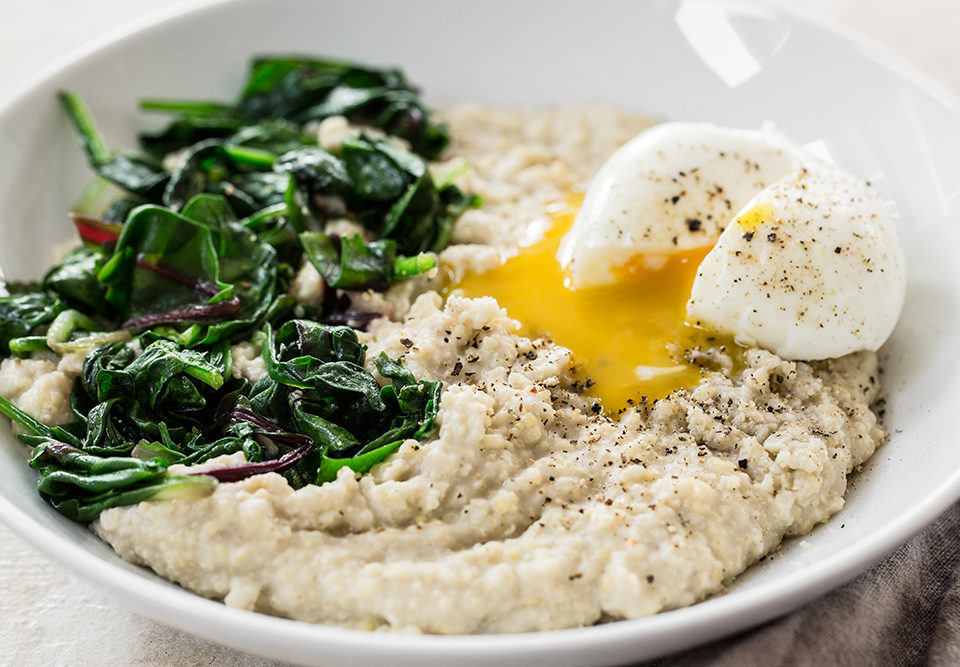

Millet Porridge
Millet porridge is a common breakfast dish, prepared by boiling millet grains until they become soft and creamy. It is often served with milk or yogurt.
Here are some typical foods and dishes you might find in Mauritania:
Lamb or Camel Meat: Lamb and camel meat are commonly used in Mauritanian cuisine. They are typically grilled or roasted and seasoned with spices.
Cheb: Cheb is a traditional Mauritanian yogurt-like dairy product made from fermented milk. It is often served as a beverage or used as a base for sauces and dressings.
Bread: Bread is a fundamental part of Mauritanian meals. It is typically made from wheat and can be served with various dishes or used to scoop up stews and sauces.
Dates: Dates are a popular snack and dessert in Mauritania. They are commonly enjoyed with a cup of sweet tea.
Sweet Tea: Sweet mint tea, known as “ataya,” is a beloved beverage in Mauritania. It is brewed with green tea leaves, sugar, and fresh mint leaves and is often offered as a gesture of hospitality.
Okra Stew: Okra stew, known as “bamyah,” is a common vegetable dish in Mauritanian cuisine. Okra pods are typically cooked with tomatoes, spices, and sometimes meat.
Maghrebi Salads: Various salads made from tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, and herbs are popular accompaniments to meals. They are typically dressed with olive oil and spices.
Sousou: Sousou is a traditional Mauritanian millet-based pudding or porridge sweetened with sugar or honey. It is often flavored with spices like cinnamon.
Mauritanian cuisine reflects the country’s cultural diversity and nomadic heritage, with an emphasis on using local and readily available ingredients. Traditional preparation methods, communal dining, and the sharing of meals are essential aspects of the culinary culture in Mauritania.
Transportation 🚥
More information about this country
Choose your destination 📍🗺
Useful Links ✅



