Tanzania travel tips
Tanzania travel tips: East African nation known for diverse wildlife, Mount Kilimanjaro, and Zanzibar’s beautiful beaches. Rich culture and landscapes.
Regions 🌎
Tanzania travel tips. Here is a list of all the regions of the Tanzania.

Arusha

Dar es Salaam

Dodoma

Geita
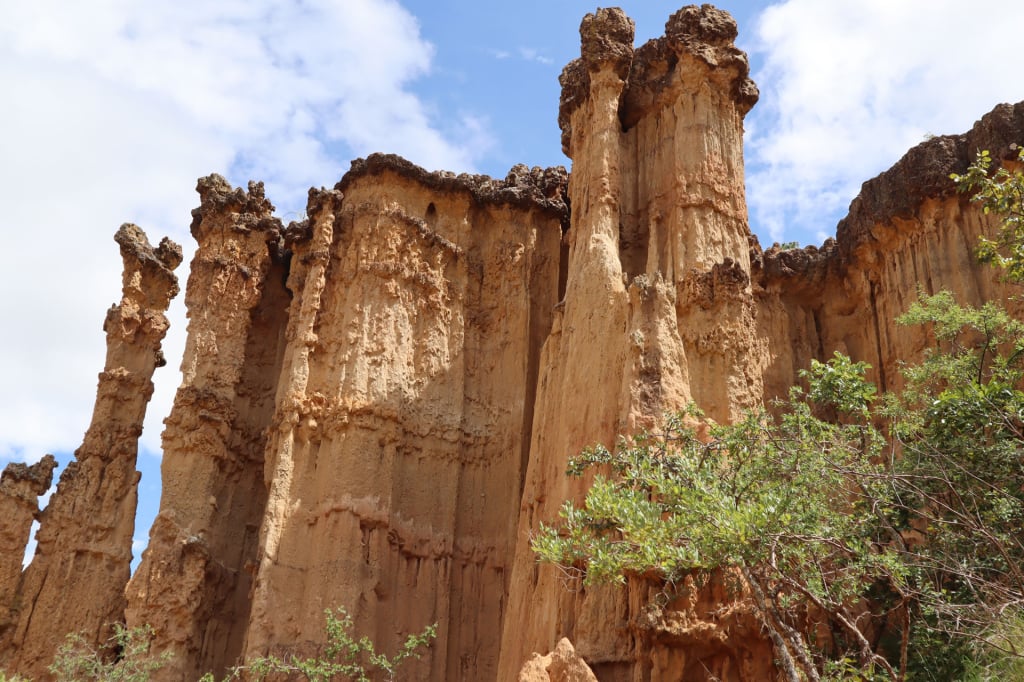

Iringa

Kagera
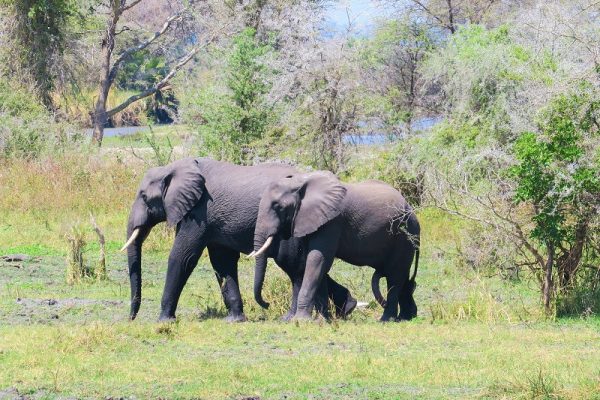

Katavi
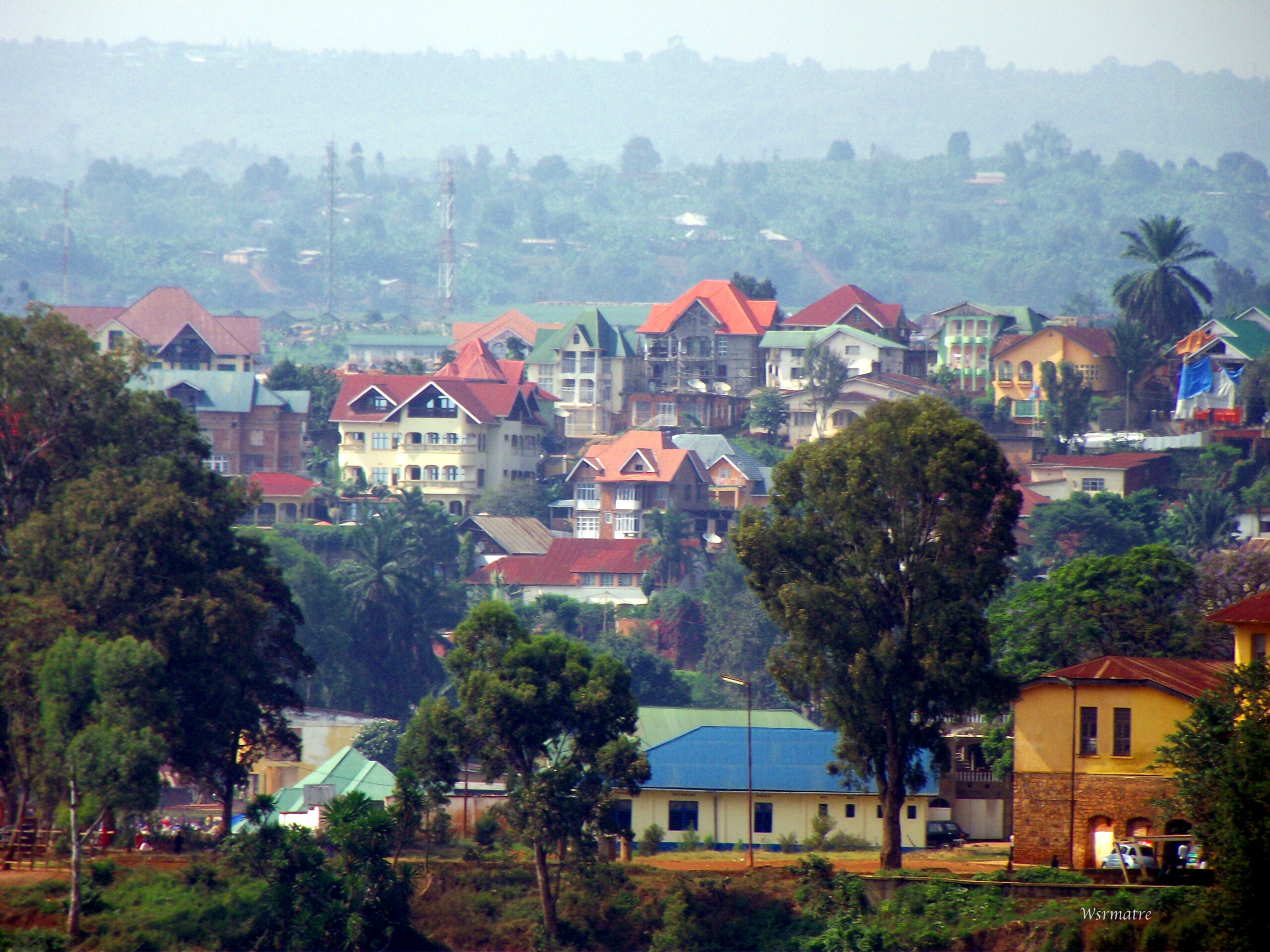

Kigoma
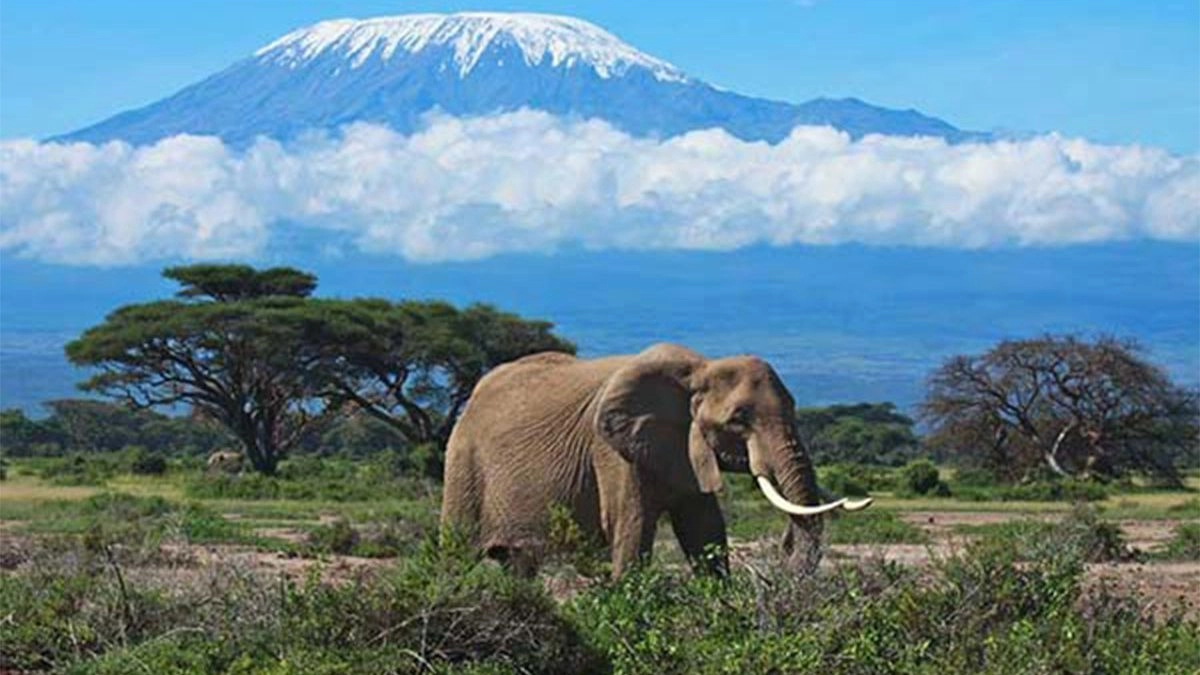

Kilimanjaro

Lindi

Manyara

Mara

Mbeya

Morogoro

Mtwara

Mwanza

Njombe

Pemba North

Pemba South

Pwani

Rukwa

Ruvuma

Shinyanga

Simiyu

Singida

Songwe

Tabora

Zanzibar Central/South

Tanga
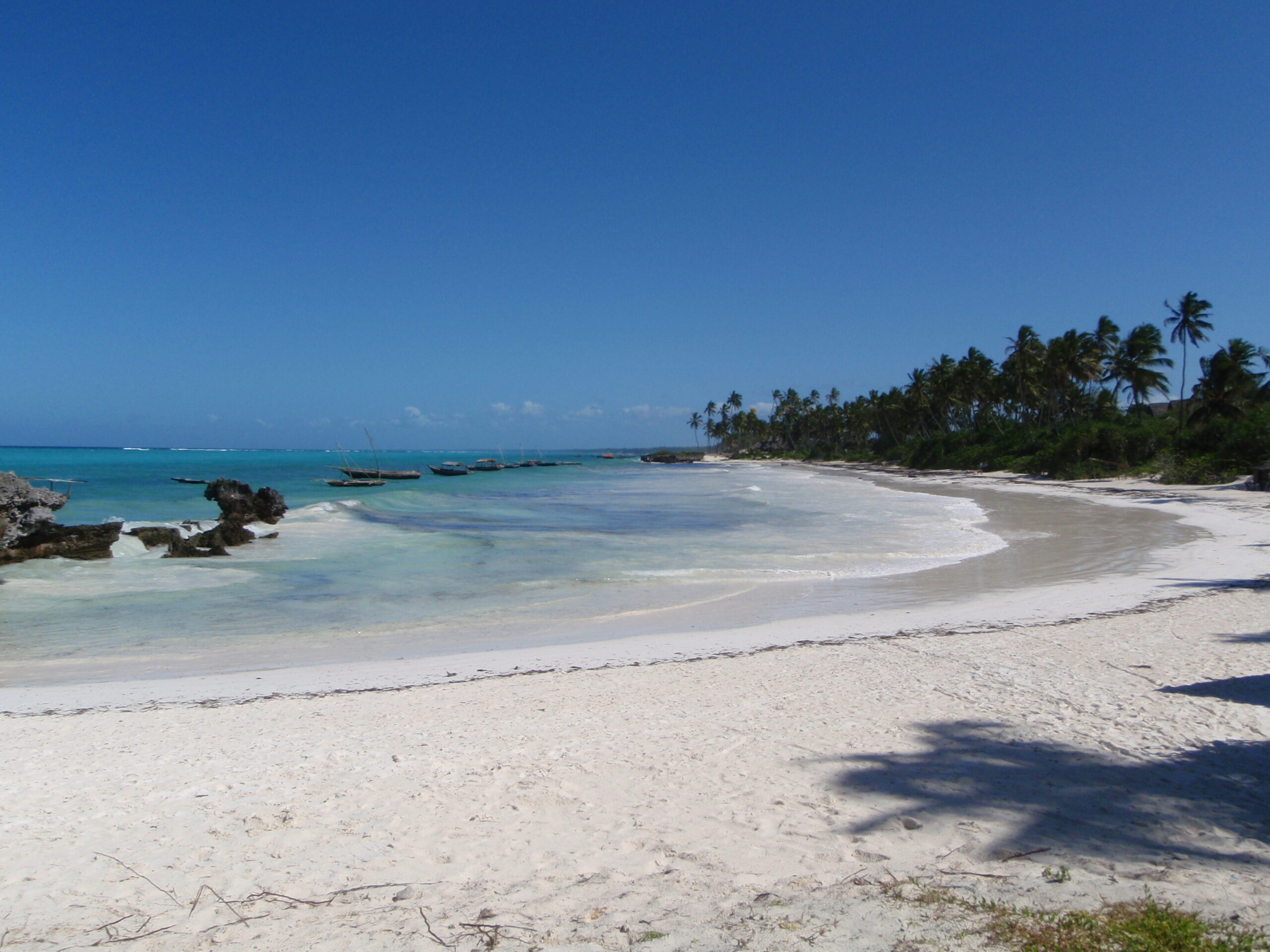

Zanzibar North
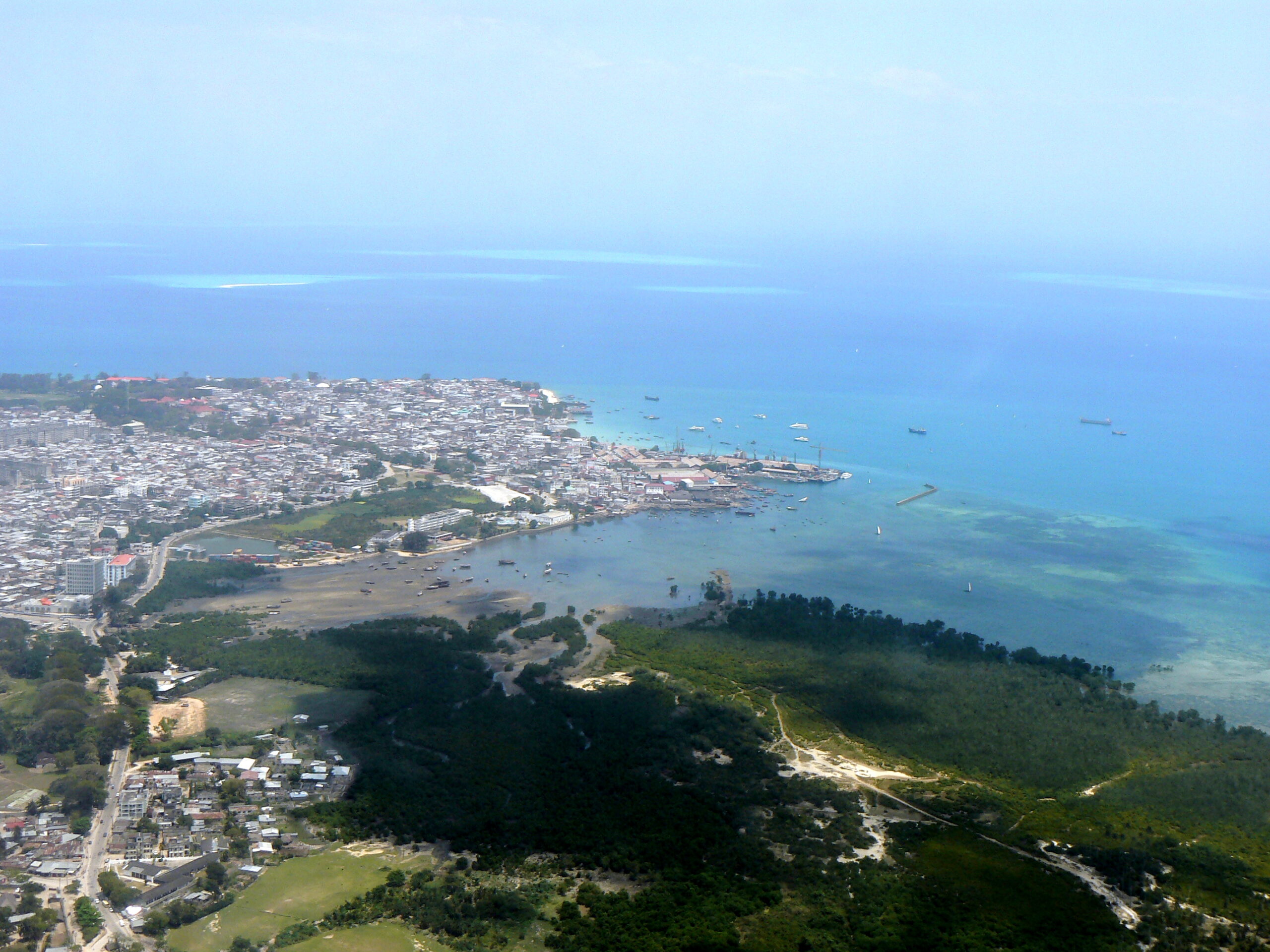

Zanzibar Urban/West
Before you go 🛩
Important information you should know before your trip
Info

Capital | Dodoma
Flag Codes:
ISO alpha-2 TZ,
ISO alpha-3 TZA
Currency
Badge | Tanzanian Shilling
CODE | TZS
NUMBER | 834
SYMBOL | Sh
FRACTION | penny
Mobile Coverage
Dialing Code | +255
SIM Card
Coverage | 3G / 4G / 5G |
Mobile Networks | Airtel Mobile | Halotel Mobile | Smile Mobile | TTCL Mobile | Zantel Mobile |
Location
Tanzania is an East African country known for its diverse landscapes, wildlife, and rich cultural heritage. It is located in the eastern part of the African continent. Here are the geographical details of Tanzania’s location:
Latitude: Tanzania spans from approximately 1 degree South latitude at its southernmost point to about 11 degrees South latitude at its northernmost point.
Longitude: The country stretches from around 29 degrees East longitude at its eastern border along the Indian Ocean to about 40 degrees East longitude at its western border with Rwanda, Burundi, and Lake Tanganyika.
Indian Ocean Coastline: Tanzania has a long coastline along the Indian Ocean, stretching for approximately 1,424 kilometers (885 miles). This coastline is known for its beautiful beaches and port cities.
Islands: Tanzania includes several offshore islands, with Zanzibar and Pemba being the most well-known. The Zanzibar Archipelago is located off the coast of mainland Tanzania and includes several islands and islets.
Tanzania’s diverse geography encompasses a wide range of environments, including the coastal lowlands, the Great Rift Valley, highland plateaus, and the famous Mount Kilimanjaro, the highest peak in Africa. The country’s natural beauty and abundant wildlife make it a popular destination for tourists and conservationists.
Currency
The currency of Tanzania is the Tanzanian Shilling, abbreviated as TZS and often symbolized as “TSh.”
The Tanzanian Shilling is further divided into smaller units, with 100 cents making up 1 Tanzanian Shilling.
Coins and banknotes are used for daily transactions in Tanzania, with various denominations available to facilitate commerce.
The currency is regulated and issued by the Bank of Tanzania, which is the country’s central bank.
When visiting Tanzania, it’s essential to have Tanzanian Shillings for local transactions, as foreign currencies are generally not accepted for everyday purchases.
Languages
Tanzania is a linguistically diverse country with numerous languages spoken by its population. However, the official languages of Tanzania are Swahili (Kiswahili) and English.
Swahili (Kiswahili):
Swahili is the national language and the most widely spoken language in Tanzania. It serves as a lingua franca, allowing people from different ethnic backgrounds to communicate with each other. Swahili is the language of instruction in primary schools, making it the first language for many Tanzanians. It is also the language used for government administration, media, and daily communication.
English:
English is the second official language of Tanzania and is used in government, education, business, and the legal system. It is often taught in schools, and many Tanzanians are bilingual, speaking both Swahili and English to varying degrees of proficiency. English is used in official documents, international relations, and as a medium of instruction in secondary and higher education.
Other languages:
In addition to Swahili and English, Tanzania is home to a wide array of indigenous languages spoken by various ethnic groups throughout the country. Some of these languages include:
Chaga (Kichaga)
Gogo (Kigogo)
Hehe (Kihehe)
Iraqw (Kiraqw)
Maasai (Maa)
Chagga (Kichagga)
Meru (Kimîrù)
Nyakyusa (Kinyakyusa)
Zaramo (Kizaramo)
Sukuma (Kisukuma)
Many others
The linguistic diversity of Tanzania reflects the rich cultural tapestry of the country, with different languages spoken in various regions and communities. Swahili, as a unifying language, plays a crucial role in national identity and communication among Tanzanians of different backgrounds.
Climate 🌡
Tanzania’s climate varies significantly across its diverse regions due to its vast geographical expanse and varying altitudes. The country experiences a range of climate zones, including tropical, savanna, arid, and temperate climates. Here is an overview of Tanzania’s main climate regions:
Tropical Coastal Climate:
The eastern coastal areas, including cities like Dar es Salaam and Tanga, have a tropical coastal climate. This region experiences high temperatures and high humidity throughout the year. Rainfall is abundant and relatively evenly distributed, with two rainy seasons: the long rains (Masika) from March to May and the short rains (Vuli) from November to December.
Tropical Savannah Climate:
Much of the central and southern parts of Tanzania, including the Serengeti and Ngorongoro Conservation Area, have a tropical savannah climate. There are distinct wet and dry seasons in these areas. The wet season typically occurs from November to May, with the heaviest rainfall in the months of March, April, and May.
The dry season runs from June to October and is the best time for wildlife viewing in national parks.
Semi-Arid and Arid Climates:
Northern and western Tanzania, including regions like Arusha, Dodoma, and Mbeya, experience semi-arid to arid conditions. These areas have less rainfall and are characterized by dry savannah and grasslands. Rainfall is more limited, and droughts are not uncommon.
Temperate Highland Climate:
Highland regions in the southern and southwestern parts of Tanzania, including Iringa and Mbeya, have a temperate highland climate. Due to higher altitudes, these areas experience cooler temperatures compared to the lowlands.
The climate is characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons, with rain primarily falling from November to April.
Lake Victoria Basin Climate:
The western part of Tanzania, particularly around Lake Victoria, experiences a climate influenced by the lake. The region has relatively higher humidity and receives more rainfall than the surrounding areas.
Rainfall occurs mainly from March to May and again from September to December.
Tanzania travel tips
If you’re planning a trip to Tanzania, here are some travel tips to enhance your experience:
Visa Requirements:
Check visa requirements and obtain necessary permits before traveling to Tanzania.
Health Precautions:
Consult a healthcare professional for vaccinations and malaria prophylaxis. Carry a basic first aid kit.
Safari Planning:
Plan safaris well in advance; consider Serengeti, Ngorongoro Crater, and Tarangire National Park for wildlife experiences.
Cultural Respect:
Respect local customs and traditions. Dress modestly, especially in rural areas, and ask before taking photos.
Transportation:
Use reputable transportation providers. Domestic flights, buses, and taxis are common. View Guide.
National Parks Regulations:
Familiarize yourself with park rules and regulations. Respect wildlife and follow ethical safari practices.
Zanzibar Exploration:
Explore Stone Town’s history and relax on Zanzibar’s beaches. Respect local customs and cover up appropriately.
Enjoy your time in Tanzania!

The best of the best
Tanzanian cuisine is diverse and reflects the country’s rich cultural heritage, incorporating flavors and ingredients from various regions and ethnic groups.

Nyama Choma
Nyama Choma means “grilled meat” in Swahili, and it is a popular dish in Tanzania.

Pilau
Pilau is a flavorful rice dish cooked with spices like cardamom, cloves, cinnamon, and cumin.
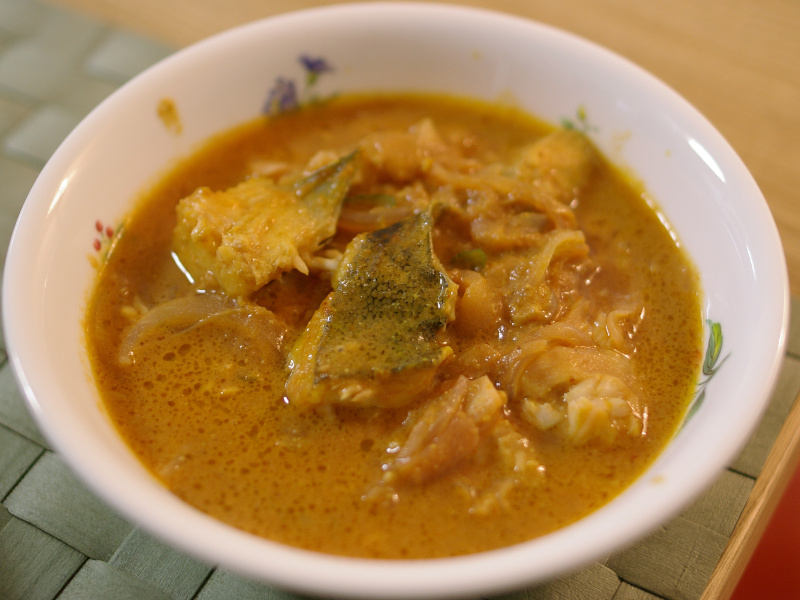

Mchuzi wa Samaki
Mchuzi wa Samaki is a spicy fish stew made with various ingredients, including fish, coconut milk, tomatoes, and spices.
Here are some typical foods and dishes you might find in Tanzania:
Chapati: Chapati is a type of flatbread that is popular in Tanzania and is often served as a side dish with various main courses.
Ndizi Nyama: Ndizi Nyama is a dish made with plantains (cooking bananas) cooked with meat, often in a tomato-based sauce.
Kachumbari: Kachumbari is a fresh and spicy tomato and onion salad that is often served as a side dish or condiment with grilled meat and other dishes.
Mishkaki: Mishkaki are skewered and grilled meat kebabs, typically made with beef, goat, or chicken.
Mbaazi wa Nazi: Mbaazi wa Nazi is a dish made with pigeon peas cooked in coconut milk, often flavored with spices like cinnamon and cardamom.
Supu ya Ndizi: Supu ya Ndizi is a plantain soup, often cooked with coconut milk and spices.
Vitumbua: Vitumbua are small, sweet rice cakes or doughnuts that are fried until golden brown and often enjoyed as a snack or dessert.
Ugali: Ugali is a staple food in Tanzania and much of East Africa. It is a stiff porridge made from maize (corn) flour and water.
Tanzanian cuisine combines a variety of flavors and ingredients, and regional variations are common. The use of spices and coconut milk is prevalent in coastal areas, while the interior regions may have dishes with a different flavor profile. Dining in Tanzania can be a delightful culinary adventure for those looking to explore East African cuisine.
Transportation 🚥
More information about this country
Choose your destination 📍🗺
Useful Links ✅



