Yemen travel tips
Yemen travel tips: On the Arabian Peninsula, is marked by diverse landscapes, historic sites, and cultural richness despite facing ongoing conflict.
Governorates 🌎
Yemen travel tips. Here is a list of all the governorates of the Yemen.

Damascus

Aleppo
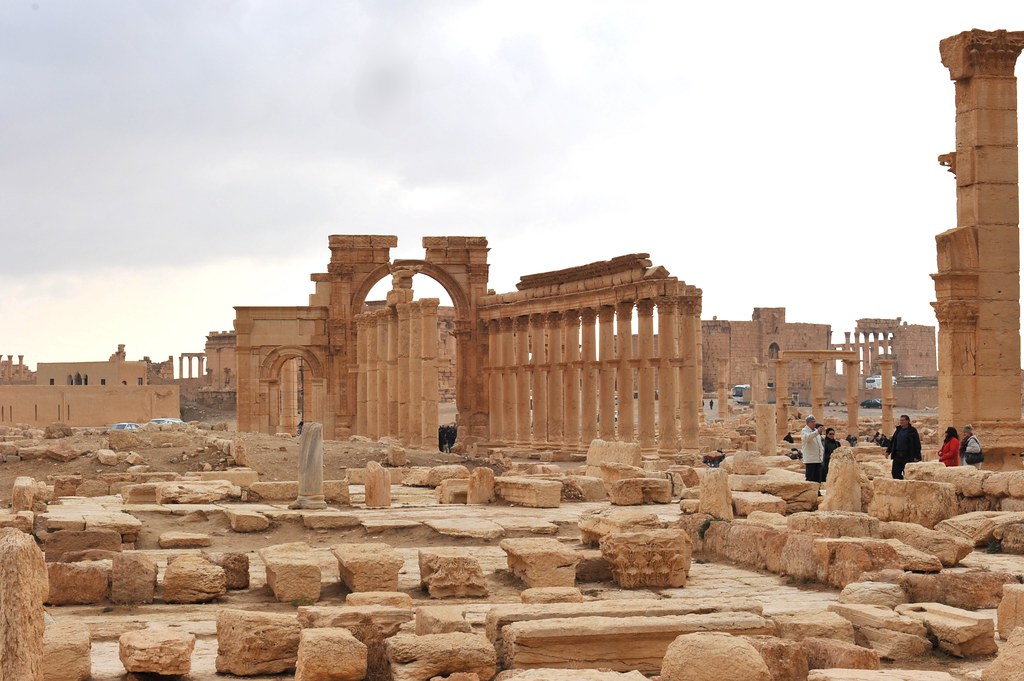

Homs
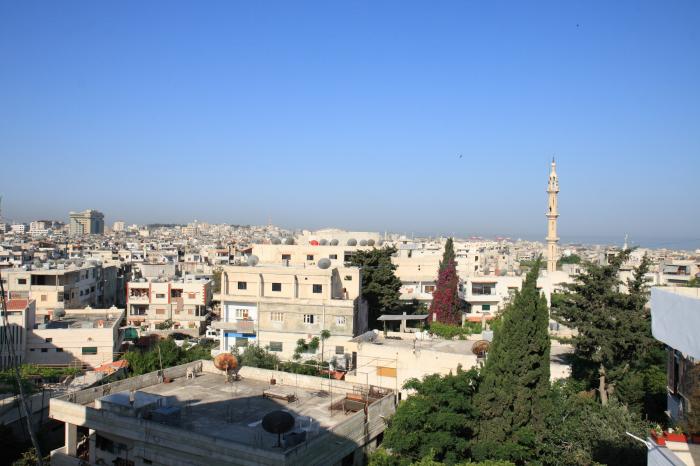

Latakia
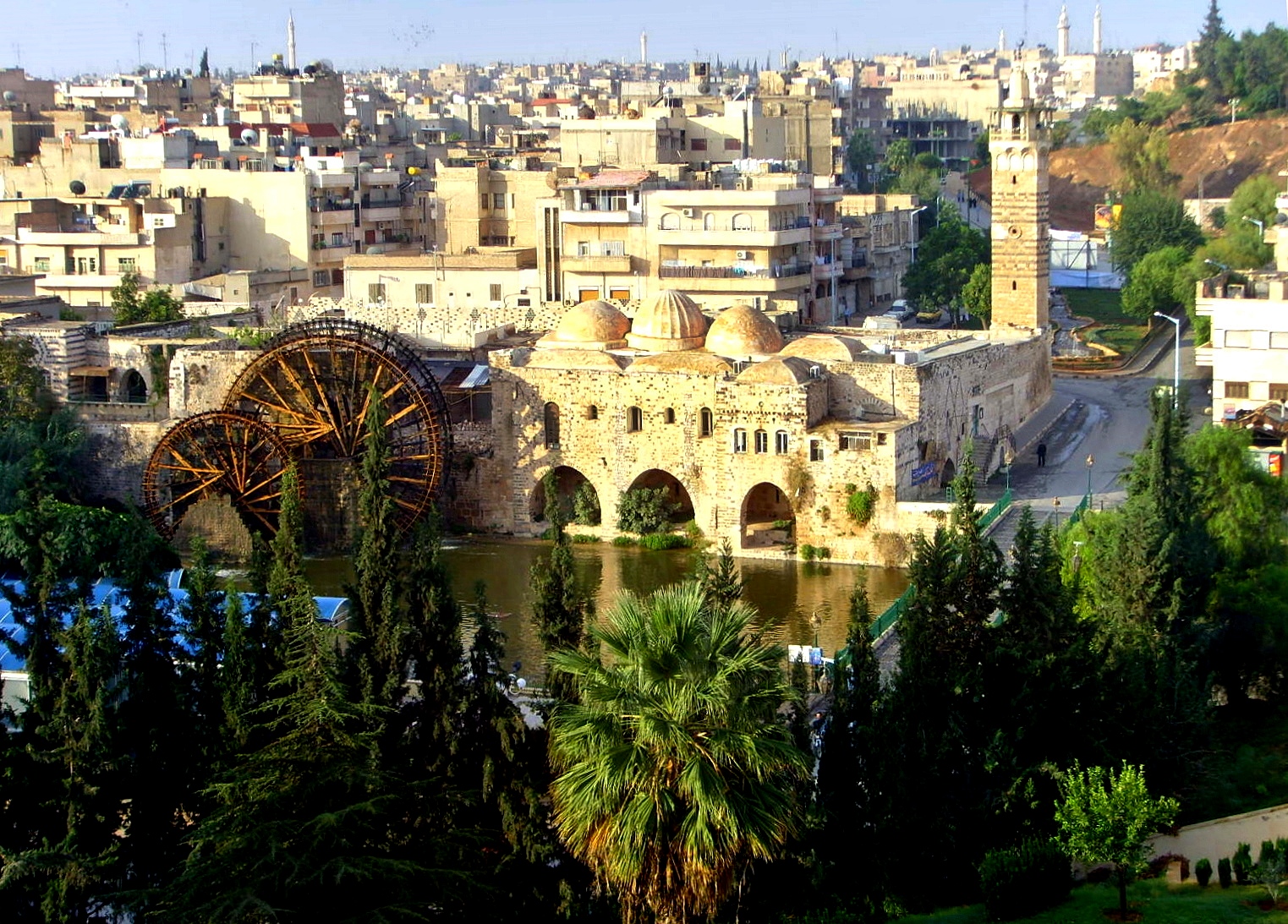

Hama

Idlib
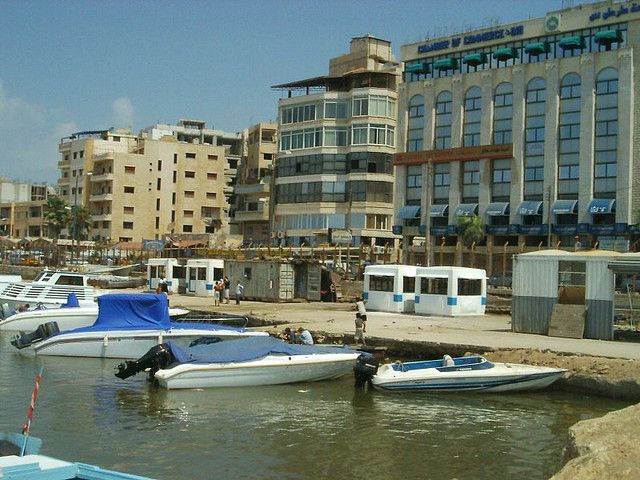

Tartus
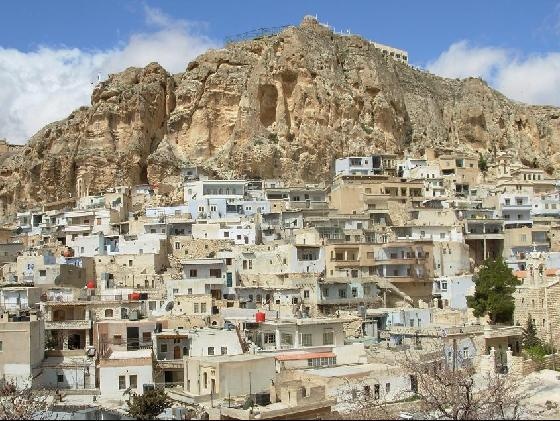

Rif Dimashq
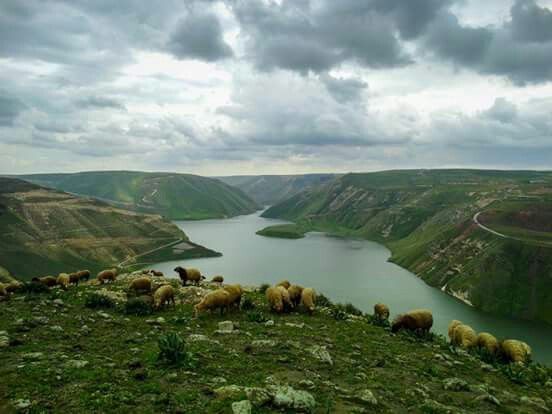

Daraa
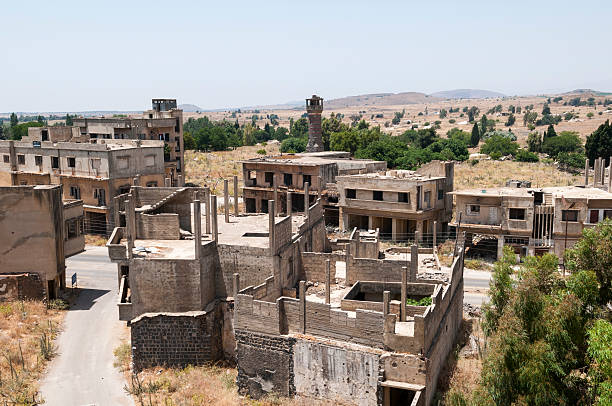

Quneitra

As-Suwayda

Deir ez-Zor

Raqqa

Al-Hasakah
Before you go 🛩
Important information you should know before your trip
Info

Capital | Sana’a
Flag Codes:
ISO alpha-2 YE,
ISO alpha-3 YEM
Currency
Badge | Yemeni rial
CODE | YER
NUMBER | 886
SYMBOL | ﷼
FRACTION | fils
Mobile Coverage
Dialing Code | +967
SIM Card
Coverage | 3G / 4G / 5G |
Mobile Networks | MTN Mobile | Sabafon Mobile | Y Mobile | Yemen Mobile |
Location
Yemen is a country located in the southern part of the Arabian Peninsula, at the southwestern tip of the Middle East. It has coastlines along the Red Sea to the west and the Gulf of Aden and the Arabian Sea to the south. Here are the geographical coordinates of Yemen: Latitude: 15.5527° N Longitude: 48.5164° E.
The capital city of Yemen is Sana’a, which is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. Yemen has a diverse geography that includes mountains, deserts, coastal areas, and fertile valleys. However, the country has faced various challenges, including political instability and conflict, in recent years. It’s important to stay informed about the current situation and travel advisories before considering any travel to Yemen.
Currency
The official currency of Yemen is the Yemeni Rial (YER), which is divided into 100 fils. However, due to political and economic instability in the country, the use of the Yemeni rial has decreased significantly and the US dollar and Saudi rial are more frequently used instead.
The banknotes available are 50, 100, 200, 250, 500 and 1,000 Yemeni rials, while the coins in circulation are 1, 5, 10, 20 and 50 Yemeni rials. In terms of design, the banknotes feature images of historical figures and emblematic places of Yemen.
It is worth mentioning that, due to the economic and political instability in Yemen, the exchange rate of the Yemeni rial can vary significantly in a short period of time and its value has decreased in relation to other international currencies. Additionally, the availability of banknotes and coins in circulation may be limited.
Languages
Arabic is the official language of Yemen and is spoken by the vast majority of the population. In addition to Arabic, several minority languages are also spoken in Yemen, such as Somali, Tigrinya, Seyyid and Mehri.
Somali is spoken by a minority in the Hadramaut region, while Tigrinya is spoken by an Eritrean minority in the Haraz region. Seyyid is spoken by a minority in the Sa’dah region, while Mehri is spoken by a minority in the Mahra region.
In summary, Arabic is the official and predominant language in Yemen, while the most widely spoken minority languages are Somali, Tigrinya, Seyyid and Mehri.
Climate 🌡
Yemen has a diverse climate influenced by its varied topography and geographical features. The country’s climate ranges from arid and desert-like conditions in many areas to more moderate conditions in highland regions. Here are the key features of Yemen’s climate:
Desert Climate:
Much of Yemen, especially the coastal and lowland areas, experiences a desert climate. This includes the Tihama coastal plain and areas along the Red Sea coast. Summers are extremely hot, with temperatures often exceeding 40°C (104°F), while winters are warm.
Highland Climate:
The central highland regions, including cities like Sana’a, have a more moderate climate due to their higher elevations. Summers are warm, and temperatures are generally milder compared to the lowland areas. Winters can be cool, and temperatures can drop significantly, especially at night.
Rainfall:
Yemen’s rainfall patterns are highly variable and influenced by the monsoon winds. Coastal areas along the Red Sea receive minimal rainfall, while the southern parts of the country experience more rain due to the influence of the Indian Ocean monsoon. The central highlands, particularly the western-facing slopes, receive more significant rainfall.
Droughts:
Yemen is prone to droughts, and water scarcity is a significant challenge in many parts of the country. The lack of reliable water sources contributes to the arid conditions in many areas.
Monsoon Season:
The southern and southeastern parts of Yemen experience a monsoon season, particularly from June to August, when the Indian Ocean monsoon brings increased rainfall and some relief from the arid conditions.
Sana’a Climate:
Sana’a, the capital city located in the highlands, has a temperate climate. Summers are mild, and temperatures rarely exceed 30°C (86°F). Winters can be chilly, with temperatures dropping to around 5°C (41°F) or lower at night.
Coastal Areas:
Coastal regions along the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea experience higher humidity levels compared to inland areas. These regions are also more influenced by monsoon winds.
Seasons:
Yemen experiences distinct seasons: hot and dry summers, and cooler winters. However, the central highlands have a more temperate climate compared to the arid lowlands.
Yemen travel tips
If you’re planning a trip to Yemen, here are some travel tips to enhance your experience:
Visa Requirements:
Obtain the necessary visas before traveling to Yemen.
Safety First:
Check travel advisories and local conditions regularly due to ongoing conflict.
Health Precautions:
Consult a healthcare professional for vaccinations and carry necessary medications.
Cultural Sensitivity:
Respect local customs, dress modestly, and seek permission before taking photos.
Transportation:
Yemen’s transportation is challenged by conflict; limited infrastructure, disrupted services, and cautious travel planning are essential for visitors. View Guide.
Electricity:
Yemen uses the Type A, Type D, and Type G electrical sockets. Bring necessary adapters.
Local Etiquette:
Greet people with politeness and follow traditional customs.
Enjoy your time in Yemen!

The best of the best
Yemeni cuisine reflects the country’s rich history, diverse cultural influences, and geographical location. Yemeni food is known for its bold flavors, aromatic spices, and use of simple, staple ingredients.

Mutabbaq
Flaky pastries filled with ingredients like spiced meat, vegetables, and sometimes cheese.

Saltah
A traditional Yemeni stew made with a base of meat (often lamb or chicken), vegetables, and a mixture of spices.
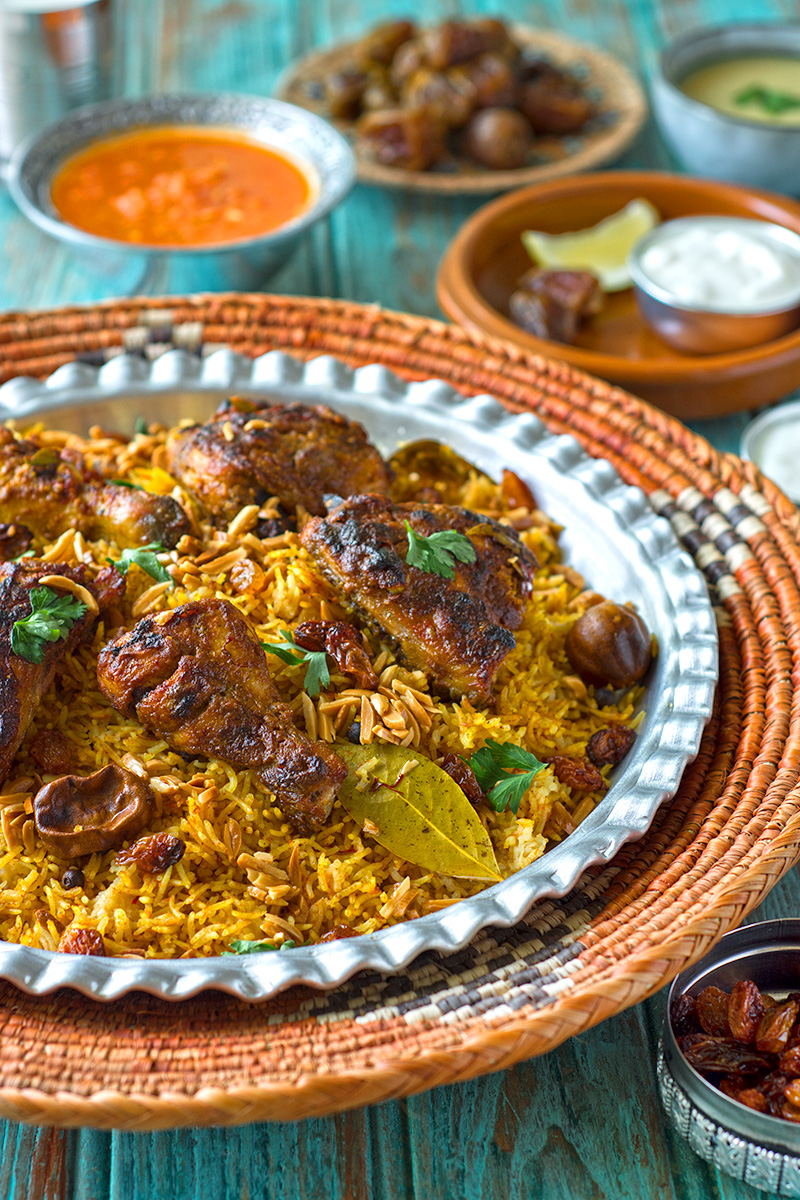

Mandi
A popular dish featuring tender meat (usually lamb or chicken) cooked with a blend of spices and served on a bed of fragrant rice. Mandi is often slow-cooked in an underground clay oven.
Here are some typical foods you might find in Yemen:
Ful Medames: Cooked fava beans served with olive oil, lemon juice, and spices. It’s often eaten for breakfast or as a snack.
Zurbian: A flavorful rice dish cooked with meat (often chicken) and spices. It’s a festive dish and can include ingredients like raisins, almonds, and saffron.
Salta Hadda: A variation of the saltah stew, featuring fish as the main protein. It’s a popular choice in coastal regions.
Sambusa: Similar to samosas, these are savory pastries filled with a mixture of meat, vegetables, and spices.
Shafout: A traditional Yemeni dessert made from fermented yogurt mixed with honey, ghee (clarified butter), and spices.
Bint Al-Sahn: A sweet honey cake often enjoyed during celebrations and special occasions.
Jachnun: A dish of rolled dough that’s slow-cooked and served with honey or other sweet toppings.
Majboos: A rice dish cooked with spices and meat, similar to biryani, that’s enjoyed in Yemen with variations across the region.
Lahoh: A type of soft, spongy flatbread often served with stews and other Yemeni dishes.
Samak Mofa: Grilled fish seasoned with spices and served with rice.
Yemeni cuisine embraces traditional methods of cooking, such as tandoor ovens and slow cooking, which contribute to its distinct flavors.
Transportation 🚥
More information about this country
Choose your destination 📍🗺
Useful Links ✅



